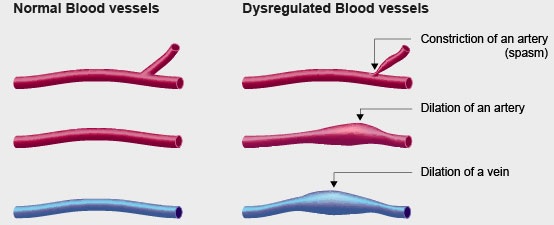
Vasospasm: Reversible constriction of an artery.
Vasospastic syndrome: Spasm in several organs of the same individual.
Vascular dysregulation: General dysregulation (too strong/weak reactions) of arteries, veins or capillaries.
Secondary vascular dysregulation (SVD): Vascular dysregulation resulting from diseases.
Primary vascular dysregulation (PVD): Dysregulation occurring in morphologically unchanged vessels in healthy subjects; this is a - most likely inherited - predisposition to react differently to a number of stimuli. The symptoms and signs increase during puberty and weaken when aging.
Flammer syndrome: Encompasses PVD together with other vascular and nonvascular signs and symptoms.
Neither the Flammer syndrome nor PVD should be confused with Raynaud's disease or Raynaud's phenomenon. The differences have been described in the scientific literature (see Literature)